Design Patterns Every Developer Must Master to Thrive in the AI Era
Tue Dec 09 2025 - 8 mins read
As AI rapidly moves from research labs into mainstream products, software developers face a new reality:
You can no longer build production systems without understanding AI-specific design patterns.
From prompt pipelines and retrieval-augmented architectures to multi-agent orchestration, the AI era is rewriting what it means to be a developer. The engineers who understand these evolving patterns will shape the next generation of intelligent software.
So, which design patterns are essential to learn?
Let’s break them down : clearly and practically.
1. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) Pattern
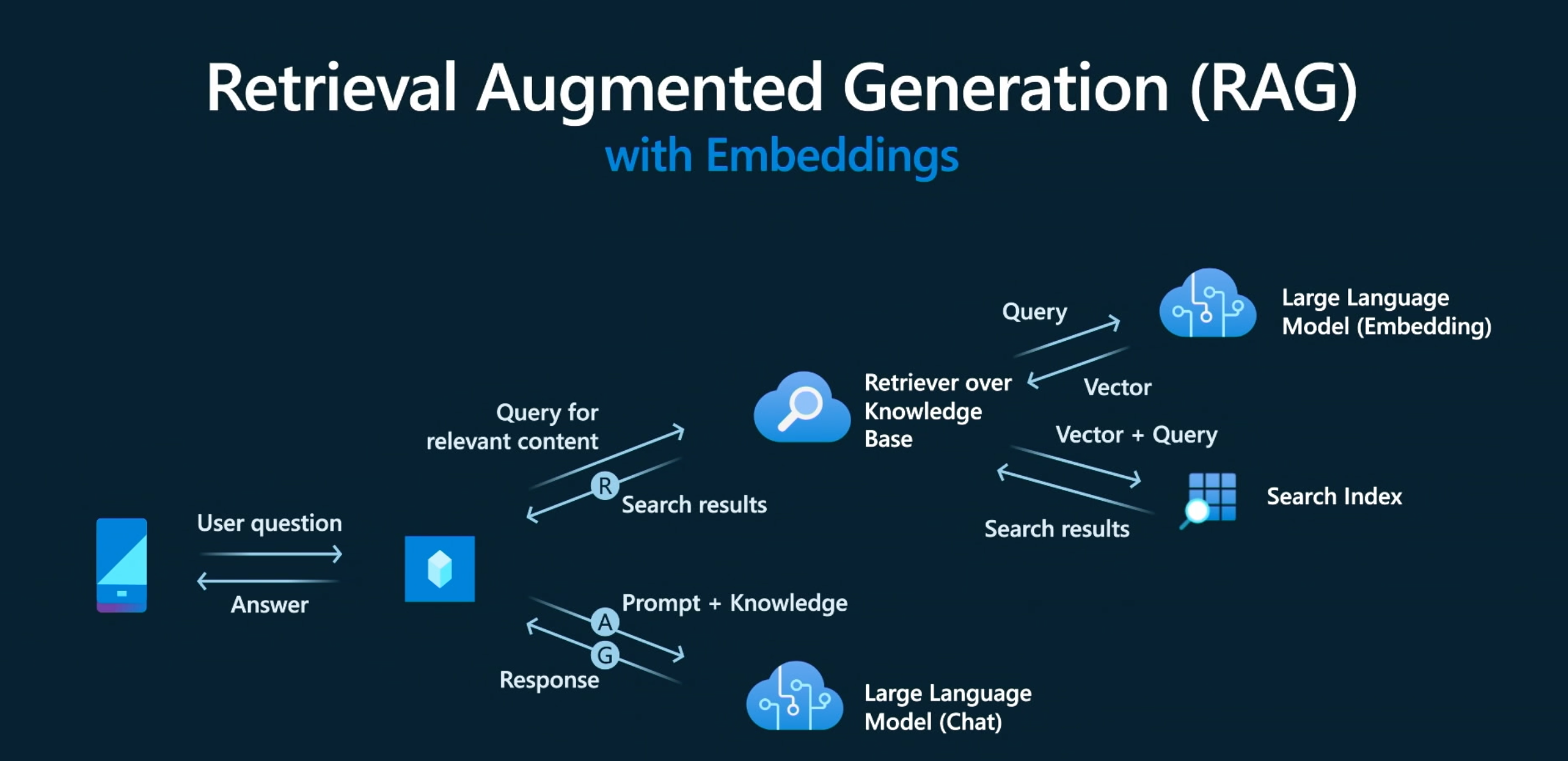
RAG has become the cornerstone of modern AI systems.
Instead of relying on LLM memory alone, RAG:
- Fetches relevant documents
- Injects them into the prompt
- Produces answers grounded in factual data
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI design pattern that improves the accuracy, reliability, and freshness of responses from language models. Instead of relying only on pre-trained knowledge, RAG allows an AI system to retrieve relevant information from an external source:such as a database, documents, or a search index:while generating answers. This makes the output far more grounded and reduces hallucinations.
Here’s how it works in simple terms: when a user asks a question, the system first searches through a knowledge base to find the most relevant pieces of information. These retrieved snippets are then passed to the language model, which combines them with its reasoning capabilities to produce a final answer. The model does not need to memorize everything; it only needs to interpret the retrieved facts and respond intelligently.
RAG is extremely useful when information changes frequently, such as product catalogs, regulations, news, or internal company documents. Developers use it to build chatbots, search assistants, and AI tools that must provide factual, up-to-date, and context-aware answers. By blending retrieval with generation, RAG creates systems that are more trustworthy, customizable, and scalable:ensuring that AI delivers consistent, knowledge-backed results every time.
2. Prompt Chaining Pattern
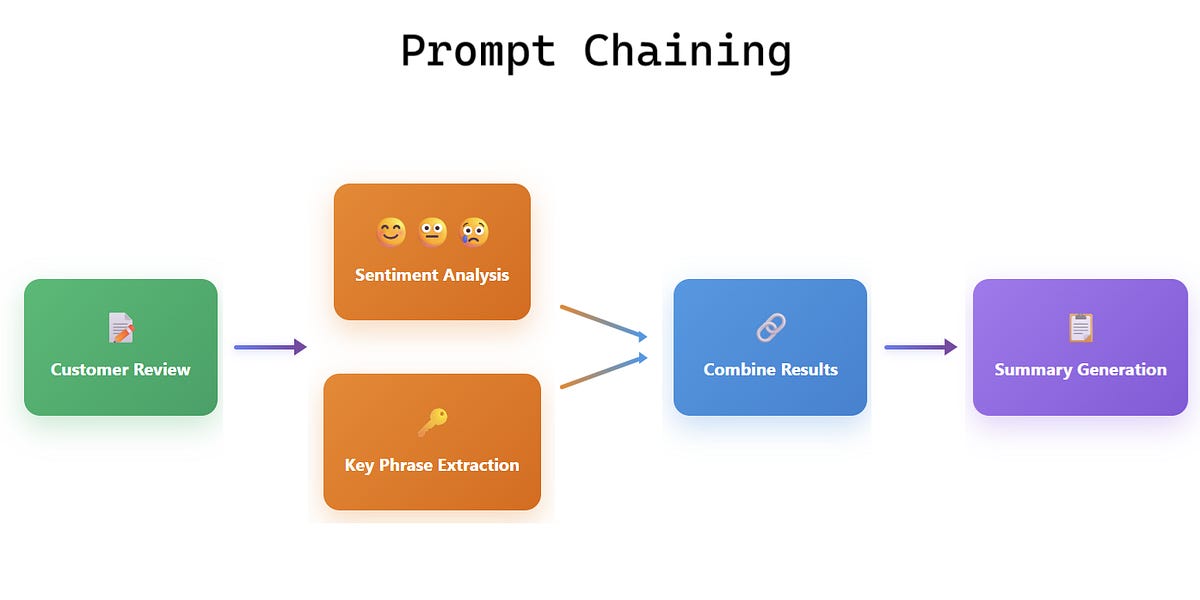
Prompt Chaining is an AI design pattern where a task is broken into multiple smaller prompts, each handled step-by-step to produce a more accurate and structured final output. Instead of asking a single large question and hoping the model gets everything right, you guide the AI through a sequence of connected prompts:like links in a chain:where each step builds on the previous one.
Here’s a simple way to understand it: imagine you want an AI to generate a full article. With prompt chaining, you might first ask it to outline the sections. Then, using that outline, you ask it to expand each section. Finally, you combine the results to form the complete article. Each prompt becomes a checkpoint, reducing confusion and improving control over the outcome.
Developers use prompt chaining when a task is complex, multi-stage, or requires consistent structure:such as summarization, data extraction, generating workflows, or building multi-step chatbots. It is also great for debugging AI behavior since you can see where the chain needs improvement.
3. Agent Orchestration Pattern
Multi-agent systems are becoming the backbone of advanced AI workflows.
This pattern allows:
- Task delegation across agents
- Error self-correction
- Tool usage coordination
- Autonomous planning
Popular frameworks already use it:
- OpenAI Agents
- LangGraph
- AutoGen
- CrewAI
Why developers must learn it:
AI will increasingly behave like a team of specialists rather than a single model.
4. Guardrails Pattern
As AI systems reach production scale, safety becomes critical.
Guardrails enforce:
- Output validation
- Format checking
- Content filtering
- Policy compliance
- Token cost control
- Prompt integrity protection
Guardrails Pattern is an AI design technique used to keep language models safe, accurate, and aligned with the intended purpose. Think of it as placing “rules on the road” so the AI doesn’t drift into harmful, irrelevant, or incorrect responses. Guardrails define what the model can and cannot do, ensuring predictable and trustworthy behavior.
In simple terms, guardrails act like filters and checkpoints. Before sending a user’s request to the AI, the system checks whether the input is allowed. After the AI generates a response, another check ensures the output follows the rules:such as avoiding personal data, preventing harmful suggestions, or sticking to factual content. If something violates these rules, the system can block the output, rewrite it, or ask the user for clarification.
Developers typically implement guardrails using predefined policies, validation scripts, classifiers, or moderation APIs. These help the AI stay within safe boundaries, especially in customer support bots, healthcare assistants, financial tools, or any system handling sensitive information.
Why it matters:
Without guardrails, your AI system will break under real-world complexity.
5. Model + Tool Hybrid Pattern
Modern AI doesn't operate alone : it uses tools.
Tools can be:
- APIs
- Databases
- Calculators
- Search engines
- Code execution sandboxes
Model + Tool Hybrid Pattern is an AI design approach where a language model works together with external tools to deliver more accurate and powerful results. Instead of relying solely on the model’s internal knowledge, this pattern allows the AI to “call” specialized tools:such as calculators, search engines, code interpreters, or APIs:to complete specific tasks.
Here’s the simple idea: language models are great at reasoning and generating text, but they are not perfect at math, real-time data lookup, or domain-specific operations. So, when a user asks a question that needs precise calculations or fresh information, the model hands that part of the request to an external tool. The tool executes the task (for example, fetching weather data or running code) and sends the result back to the model, which then combines everything into a final answer.
This hybrid approach is commonly used in chatbots, coding assistants, travel planners, financial calculators, and data-driven applications. It ensures accuracy, reduces hallucinations, and extends the model’s capabilities far beyond text generation.
6. Embedding + Vector Database Pattern
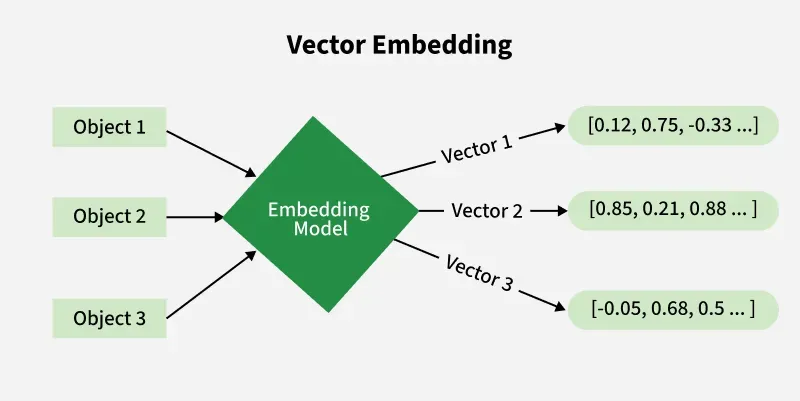
For developers, vector databases are the new “database literacy”.
This pattern includes:
- Converting text/images/code into embeddings
- Storing them in vector DBs
- Running similarity search
- Ranking contextual information
This powers:
- Personalized recommendations
- Semantic search
- Memory systems for agents
- Context-aware chatbots
Why it matters:
Almost every AI-powered product uses embeddings under the hood.
7. Prompt Template Pattern
Even though prompts feel simple, scalable systems require structured prompt templates.
Characteristics:
- Consistent variable slots
- System + instruction separation
- Memory-aware design
- Guarded formatting
- Reusable prompt components
Prompt Template Pattern is an AI design technique where you create reusable, structured prompt formats to guide a language model consistently. Instead of writing new prompts every time, you prepare a template with placeholders that can be filled with dynamic data:making the AI’s responses more predictable, repeatable, and aligned with your goals.
Here’s the simple explanation: imagine you need to generate product descriptions, summaries, or code explanations repeatedly. Instead of crafting a unique prompt each time, you use a template like: “Write a short description for: {{product_name}}. Highlight these features: {{features}}. Keep the tone {{tone}}.” Whenever you fill the placeholders, the model knows exactly how to respond. This reduces confusion and ensures high-quality, consistent outputs.
Prompt templates are extremely useful in chatbots, content generation tools, customer support systems, and workflow automation. They help maintain tone, structure, and accuracy across thousands of responses. Developers often combine them with variables, conditionals, or dynamic data to adapt prompts to different scenarios.
8. Model Ensemble Pattern

Similar to classical ML ensembles, AI engineers now combine models like:
- LLM + vision model
- LLM + embeddings model
- LLM + classifier
- Multiple LLMs voting
This increases:
- Accuracy
- Reduction of hallucinations
- Domain specialization
- Reliability in mission-critical apps
Why it matters:
One model alone is rarely enough for robust solutions.
9. Self-Reflection / Self-Healing Pattern
This advanced pattern allows AI systems to:
- Critique their own answers
- Improve them with a second pass
- Fix reasoning errors
- Validate outputs before returning
It mirrors human problem-solving:
Think → Check → Improve → Finalize
Used heavily in:
- Code generation
- Math reasoning
- Report writing
- Long-form workflows
Why learn this:
It’s one of the simplest ways to boost model quality without upgrading hardware.
10. Data Flywheel Pattern
In AI, products improve automatically through usage.
This pattern creates a loop:
- Collect user interactions
- Use feedback to refine prompts, models, or embeddings
- Improve predictions
- Attract more users
- Generate more data
Products like Notion AI, GitHub Copilot, and ChatGPT follow this flywheel.
Data Flywheel Pattern is an AI growth strategy where your system continuously improves by learning from the data generated through real user interactions. Think of it like a self-reinforcing loop: more users create more data, more data improves the model, and a better model attracts even more users. Over time, this creates a powerful cycle that accelerates performance and innovation.
Here’s the simple explanation: when users interact with an AI system:asking questions, giving feedback, correcting mistakes, or uploading content:they generate useful data. This data (after being cleaned and anonymized) is fed back into the system to retrain or fine-tune the model. As the model becomes smarter, it provides more accurate, personalized, and helpful responses. This leads to increased engagement, which creates even more high-quality data.
Companies use the Data Flywheel Pattern in search engines, recommendation systems, e-commerce platforms, chatbots, and productivity tools. For example, every product click on Amazon, every playlist like on Spotify, or every feedback given to an AI assistant reinforces the flywheel.
The Data Flywheel Pattern is powerful because it creates compounding returns. The system keeps getting better automatically, reducing manual work and driving long-term competitive advantage through continuous learning and refinement.
The AI field is evolving fast : but the developers who master these patterns will always be relevant.
AI success is no longer just about learning Python or React.
It’s about understanding:
- Architectures
- Systems thinking
- Agent coordination
- Data workflows
- Prompt engineering at scale
In the coming decade, companies won't just hire “AI developers.” They will hire engineers who understand AI architecture. And learning these design patterns is the first major step.
Tue Dec 09 2025




